What is Lead Time Exactly?
Supplier lead times refer to the total time from when a buyer places an order with a supplier to when the goods or materials are delivered. It encompasses several stages, including order processing, production (if applicable), packaging, and shipment. For custom-made or made-to-order items, supplier lead time may also include manufacturing time. Whereas for off-the-shelf products, it primarily consists of time for order fulfillment and shipping. This lead time is critical in supply chain management, as it impacts inventory control, production planning, and the ability to meet customer demand.
Effective management of supplier lead times ensures that materials arrive on schedule, helping to avoid production delays, stockouts, or excess inventory. Factors influencing lead times include the supplier’s capacity, product complexity, shipping method, and the distance between the supplier and the buyer. For international orders, customs clearance and import/export regulations can further extend lead times. Businesses often negotiate or track lead times closely to improve efficiency and reduce costs associated with supply chain disruptions.
Why Supplier Delivery Lead Times Matter
Management of supplier delivery lead times plays a large part in guaranteeing smooth operations in manufacturing and supply chain management. Unpredictable lead times can disrupt production schedules, increase inventory requirements, and impact customer satisfaction.
Managing delivery lead times is essential for effective production planning. When delivery times are long or unpredictable, it can cause significant disruptions to production schedules if materials or components do not arrive as expected. This can result in delayed manufacturing, increased downtime, and costly rescheduling efforts. Ensuring that materials are delivered on time allows production to run smoothly and meet deadlines.
Lead times also play a crucial role in inventory management. Companies must factor in delivery lead times when determining reorder points and calculating the necessary safety stock to avoid running out of materials. If lead times are longer, businesses may need to carry more inventory. This ties up capital and increases storage costs. Properly managing lead times helps companies maintain optimal inventory levels and avoid stockouts that could halt production.
Balancing cost and efficiency is another important reason to manage lead times. While faster delivery options, such as air freight, can reduce lead times, they tend to be more expensive. Businesses must weigh the cost of faster deliveries against the need to meet production deadlines or fulfill customer orders quickly. Managing lead times effectively can help find the right balance between cost control and operational efficiency.
Finally, reliable delivery lead times are critical for maintaining customer satisfaction, especially for companies using Just-In-Time (JIT) or lean manufacturing strategies. In these systems, materials need to arrive precisely when needed to keep production moving without excess inventory. If delivery times are uncertain or longer than expected, it can disrupt downstream processes, delay product shipments, and negatively affect customer relationships.
Key Components of Supplier Delivery Lead Times
Delivery lead times specifically refer to the amount of time it takes for a supplier to deliver goods or materials to a buyer after they have been dispatched or shipped. This is a subset of the overall supplier lead time and focuses on the time needed for physical transportation and delivery once the order is ready for shipment. Still, this metric can comprise of a number of aspects that affect when deliveries arrive.
1. Shipping Method
Delivery lead time depends heavily on the shipping method chosen by the supplier or buyer. Common methods include:
- Ground transportation: Trucks, rail, etc. (typically used for domestic shipments).
- Air freight: Often used for faster, but more expensive international or long-distance shipments.
- Ocean freight: Common for large international shipments, but slower due to the time required for loading/unloading and ocean transit.
2. Distance and Location
Usually, the farther the supplier is from the buyer, the longer the delivery lead time. International shipments will naturally take longer than domestic shipments, especially when different continents or remote areas are involved.
3. Customs and Border Control (for international shipments)
For international shipments, goods must pass through customs clearance in both the exporting and importing countries. This process can add significant time depending on the country’s regulations, the type of goods, and any delays in paperwork or inspections.
4. Carrier Schedules
Some modes of transport, especially ocean freight, are subject to fixed schedules (e.g., weekly sailings). If goods are ready just after a shipping deadline, they may have to wait until the next available departure, adding to the lead time.
5. Handling at Ports or Distribution Centers
Time spent loading and unloading at ports, or processing at distribution centers or warehouses, can also add to delivery lead times.
6. Final Mile Delivery
Once goods arrive at the destination port or transportation hub, additional time is needed for “last-mile” delivery to the final destination. This could involve local trucking, courier services, or other means of transport.
Supplier delivery lead times are a critical factor in logistics and supply chain management, as they influence how quickly goods can be transported from the supplier’s facility to the buyer’s location after they have been shipped.
Estimating Supplier Lead Times
While the easiest method may be to inquire with the vendor, buyers can estimate supplier lead times using data they already have by analyzing historical purchase order records, supplier performance metrics, and logistical details. Sometimes these estimates can be more reliable than the provided dates. Here are the key steps buyers can take to arrive at a usable lead time estimate:
1. Analyze Historical Purchase Data
Buyers can review past orders to calculate the time between placing a purchase order and the receipt of goods. By averaging the delivery times from a specific supplier over a set period (e.g., the past year), they can estimate the typical lead time. This includes looking at data points like:
- Date of order placement
- Date of supplier confirmation
- Date of shipment dispatch
- Date of delivery at the buyer’s facility
Analyzing patterns in this data will help determine the average, shortest, and longest lead times, giving a more nuanced understanding of supplier reliability.
2. Evaluate Supplier Performance
Suppliers often provide quoted lead times during the purchasing process. Buyers can compare the actual lead times (from historical data) with the quoted lead times to assess supplier consistency. If suppliers frequently miss their promised lead times, buyers may need to adjust expectations or build in a buffer period. Performance reports, such as on-time delivery rates, can offer insights into how frequently the supplier meets their commitments and whether lead times are improving or worsening over time.
3. Consider Variability Based on Order Type and Size
Different types of products or varying order sizes can impact supplier lead times. For example, a bulk order or a custom order may have longer lead times than standard, smaller orders. Buyers can use historical data to estimate lead times for different order types and adjust their expectations accordingly. Segmenting past orders by product categories, order volumes, or production complexity can help identify trends that influence lead times.
4. Factor in Transit Times
Buyers can estimate delivery lead times based on shipping methods (air, ocean, ground) and geographic distances between the supplier’s facility and their own. Historical data on how long each shipping method typically takes for different suppliers can help in calculating the transportation component of lead times. Tracking any delays due to customs, port congestion, or carrier-related issues can help refine estimates, especially for international shipments.
By combining historical data analysis, supplier performance evaluation, and logistical insights, buyers can create accurate estimates of supplier lead times and use this information to optimize inventory management and production planning.
The right tools for the job
Using Material Requirements Planning (MRP) software makes managing supplier lead times much easier for buyers by automating many procurement tasks and centralizing data. Systems like Aligni MRP provides a single platform where buyers can track supplier lead times, order histories, and delivery schedules, eliminating the need for manual record-keeping. The software can track and update lead times based on historical data, reducing errors and ensuring that procurement schedules are always aligned with current information. Additionally, MRP systems can send alerts when deliveries are delayed or when it’s time to reorder materials. This helps buyers stay on top of their supply needs and avoid costly disruptions.
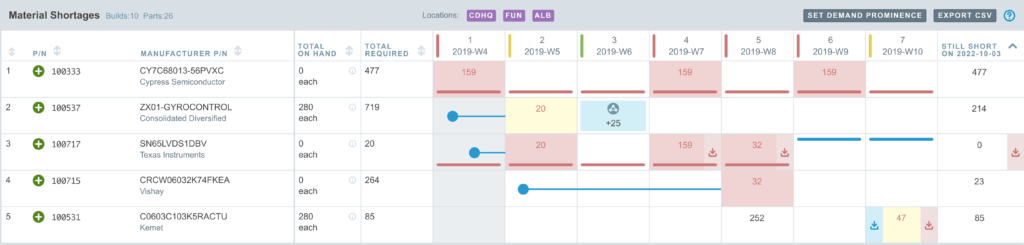
Aligni MRP software also improves demand forecasting by integrating sales forecasts and production schedules with supplier lead times. The system can help plan purchase orders based on material requirements, ensuring that supplies arrive just in time for production. This capability helps buyers avoid stockouts and excess inventory, reducing carrying costs and improving cash flow. The software helps buyers adjust procurement schedules, responding to any changes in supplier lead times, production demands, or unforeseen supply chain disruptions. This combination of data management and flexibility helps businesses maintain smooth operations even in the face of unexpected delays.
Another significant advantage of MRP software is its ability to track supplier performance. By monitoring how consistently suppliers meet their lead times, buyers can generate detailed reports on supplier reliability, which can guide future procurement decisions or negotiations. Buyers can also use this information to identify potential risks or inefficiencies in the supply chain. Furthermore, Aligni MRP software helps optimize inventory by streamlining the calculation of reorder points based on lead times and consumption rates. This ensures that materials are ordered at the right time, reducing the risk of stockouts while minimizing excess inventory.
Lastly, MRP systems enhance collaboration across departments by integrating procurement data with production, inventory management, and finance functions. This alignment ensures that all areas of the business are in sync, and procurement decisions are informed by the broader context of the company’s operations. If production schedules shift, the MRP system will adjust procurement timelines accordingly, allowing buyers to be responsive to changing needs. By streamlining these processes and providing real-time data, MRP software helps buyers manage supplier lead times more effectively, ultimately improving supply chain efficiency and reducing costs.
Taking the Next Steps
Managing supplier lead times is an important component in ensuring smooth production planning, efficient inventory management, and maintaining customer satisfaction. Long or unpredictable lead times can disrupt schedules, increase the need for excess inventory, and raise costs if faster delivery methods are required to meet deadlines. Reliable lead times are especially important, as timely deliveries are essential to avoiding production delays.
Efficiently managing lead times requires collecting a large amount of data and processes to turn it into usable insights. This is easy to do with a small amount of parts or vendors. When the complexity increases, keeping up with the data becomes almost impossible. In these occasions, using MRP software like Aligni is essential for effectively managing these lead times, as it automates tracking, optimizes procurement schedules, and provides real-time adjustments, helping businesses maintain efficiency and reduce costs across the supply chain.
If you are ready to turn your purchasing data into insights and maybe a competitive advantage, it is time to get the right tool for the job. Sign up for Aligni MRP today!
Start your 30-day free trial
Helping You Make Great Things…Better.

